Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions in a secure and transparent manner across a network of computers.
It enables secure and transparent transfer of information without the need for a central authority, making it ideal for various applications such as cryptocurrency transactions, secure record-keeping, and supply chain management.
In today’s article you will know what is blockchain, how does blockchain work, what is its scope in future
Apart from this, what is blockchain security, which companies use blockchain or what are its advantages and disadvantages.
What is Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is a decentralized, digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. It allows for secure and transparent transfer of digital assets without the need for intermediaries, as each transaction is verified and recorded on multiple computers in the network.
The key feature of blockchain technology is its use of cryptography to secure the transactions and maintain the integrity of the ledger. The transactions are grouped into blocks, which are then cryptographically linked together to form a chain of blocks, hence the name “blockchain”.
Blockchain technology was first introduced as the underlying technology for the Cryptocurrency Bitcoin, but its potential applications go beyond just digital currencies.
It is being explored for use in various industries, such as finance, supply chain, healthcare, and voting systems, due to its potential to increase transparency, security, and efficiency in these areas.
Explanation of Blockchain For Beginners
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. It was first introduced as the underlying technology behind the cryptocurrency Bitcoin, but has since been adopted for a variety of other uses.
Here’s how blockchain works:
- Transactions: When someone wants to make a transaction, they send it to the network of computers that make up the blockchain.
- Validation: The transaction is then verified by multiple computers in the network, called “nodes.”
- Recording: Once a transaction has been validated, it is added to a “block,” which is a collection of transactions.
- Linking: The block is then linked to the previous block in the chain, creating a secure and unbreakable link between all the blocks in the chain.
- Decentralization: The blockchain is decentralized, meaning there is no central authority controlling it. This makes it highly secure, as any changes to the information on the blockchain would have to be made by the consensus of the nodes in the network.
In short, blockchain technology allows for secure and transparent record-keeping, making it useful for a variety of applications beyond just cryptocurrency.
Whether you’re making a financial transaction, sharing medical records, or tracking a supply chain, blockchain can help ensure the security and transparency of the information being shared.
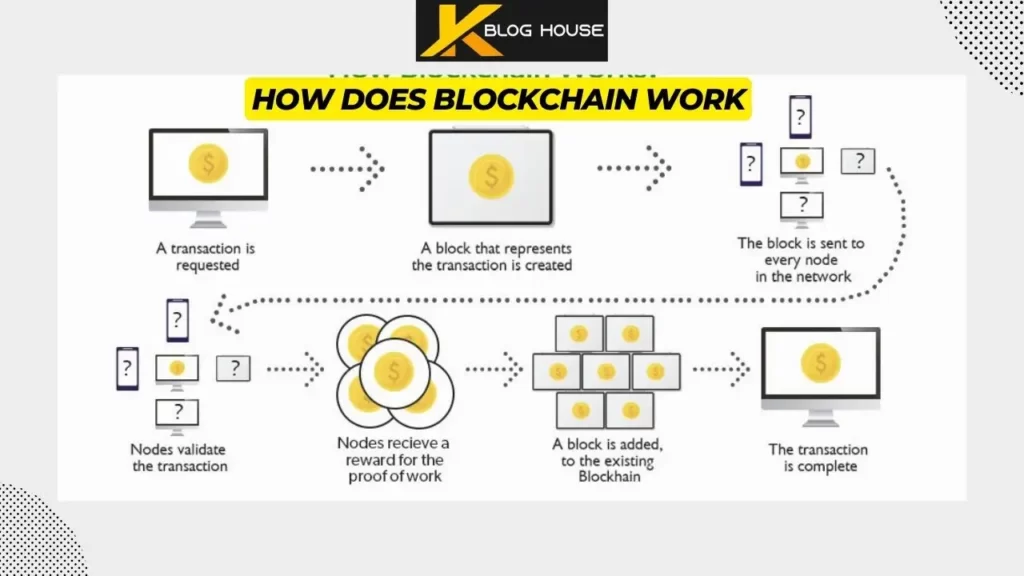
How Does Blockchain Work
Blockchain works by allowing transactions to be recorded on a decentralized ledger that is maintained by a network of computers. Each transaction is verified by multiple computers on the network and once verified, is grouped with other verified transactions into a block.
This block is then cryptographically linked to the previous block in the chain, forming a secure and permanent record of all transactions.
Here is a simple explanation of the process:
- A transaction is initiated between two parties.
- The transaction is broadcast to the network and verified by multiple computers, called “nodes”.
- The verified transactions are grouped into a block and added to the blockchain.
- The block is then encrypted using complex algorithms to secure the transactions and ensure the integrity of the ledger.
- The block is added to the chain of previous blocks, forming a permanent and unalterable record of all transactions.
Because the ledger is maintained by a decentralized network of computers, there is no central authority or single point of control.
This makes it highly secure and resistant to tampering or hacking, as any attempt to alter the record would require the attacker to take control of the majority of the nodes on the network.
This decentralized structure also ensures transparency, as all participants on the network have a copy of the ledger and can verify the validity of any transaction. This creates trust in the system, as all parties have access to the same information.
Real Life Uses Of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has a wide range of potential uses beyond just digital currencies, and many industries are exploring its potential applications.
Here are some real-life examples of how blockchain technology is being used:
- Finance: Blockchain technology is being used to create secure, transparent, and efficient financial systems. For example, it can be used to track and settle transactions in real-time, reducing the need for intermediaries and improving the overall efficiency of the financial system.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain technology can be used to track goods and products as they move through the supply chain, increasing transparency and accountability. For example, a blockchain-based system could be used to track the origin and journey of food products, ensuring that they are safe and ethically sourced.
- Healthcare: Blockchain technology can be used to securely store and manage medical records, improving the accessibility and security of patient information.
- Identity Management: Blockchain technology can be used to create secure and decentralized systems for managing personal identity information, reducing the risk of data breaches and increasing privacy.
- Voting: Blockchain technology can be used to create secure and transparent voting systems, reducing the risk of fraud and increasing voter confidence.
- Real Estate: Blockchain technology can be used to track and manage property transactions, making the process faster, more secure, and more transparent.
- Gaming: Blockchain technology can be used to create secure and transparent systems for in-game transactions, improving the overall gaming experience.
These are just a few examples of the potential uses of blockchain technology. As the technology continues to evolve and mature, it is likely that even more innovative and practical applications will be developed in the future.
Types of Blockchain
There are several different types of blockchain, each with its own unique characteristics and uses. Here are the most common types of blockchain:
- Public Blockchains: Public blockchains, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, are decentralized and open to everyone. They are transparent, secure, and maintained by a large network of nodes. Transactions are processed and verified by the nodes, and the ledger is available for anyone to view.
- Private Blockchains: Private blockchains, also known as permissioned blockchains, are designed for use within a specific organization or consortium. They are maintained by a smaller, trusted group of nodes, and access to the ledger is restricted to authorized participants. Private blockchains offer a high degree of privacy and security, but also have a lower degree of decentralization and transparency.
- Consortium Blockchains: Consortium blockchains are a hybrid of public and private blockchains, designed for use by a specific consortium or group of organizations. They are maintained by a group of nodes, with access to the ledger being restricted to authorized participants. Consortium blockchains offer a good balance between privacy, security, and decentralization.
- Hybrid Blockchains: Hybrid blockchains are blockchains that incorporate elements from both public and private blockchains. They offer the benefits of both public and private blockchains, and can be designed to meet the specific needs of different organizations and use cases.
Each type of blockchain has its own unique advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which type to use will depend on the specific needs and requirements of the organization or consortium in question.
Comparison of Blockchain and Cryptocurrency
Blockchain technology and Cryptocurrency are often discussed together, as cryptocurrency is one of the most well-known and widely-used applications of blockchain.
A cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual asset designed to work as a medium of exchange that uses cryptography to secure its transactions and control the creation of new units.
Bitcoin was the first decentralized cryptocurrency, and it remains one of the most well-known and widely-used cryptocurrencies today.
Blockchain technology provides the infrastructure for cryptocurrencies to exist and function, by allowing for the secure and transparent recording of transactions on a decentralized ledger.
This ledger is maintained by a network of computers, and each block in the chain contains a record of multiple transactions. Once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered, creating a permanent and tamper-proof record of all transactions.
The combination of blockchain technology and cryptocurrency has the potential to disrupt many traditional financial systems and intermediaries, by enabling secure and transparent transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks.
However, the use of Cryptocurrency and blockchain technology is still in its early stages, and there are many challenges and risks that need to be addressed before it can reach its full potential.
Differences Between Blockchain and Traditional Databases
Blockchain and Traditional Databases are both methods of storing and organizing data, but they have several key differences. Here are some of the main differences between blockchain and traditional databases:
- Decentralization: A traditional database is centralized, meaning that it is controlled and maintained by a single entity or organization. Blockchain, on the other hand, is decentralized, meaning that it is maintained by a network of computers, without a central authority.
- Security: Traditional databases are vulnerable to hacking, tampering, and other security breaches, since they are maintained by a single entity. Blockchain, on the other hand, uses cryptographic algorithms and a decentralized network to secure its transactions and protect against tampering and hacking.
- Transparency: Traditional databases are typically private and not transparent, with access restricted to authorized individuals or organizations. Blockchain, on the other hand, is transparent, allowing all transactions to be publicly visible on the ledger.
- Immutability: Traditional databases can be altered or deleted, making it possible for data to be lost or changed. Blockchain, on the other hand, is immutable, meaning that once data has been recorded on the chain, it cannot be altered or deleted.
- Efficiency: Traditional databases can be slow and inefficient, since they rely on a single entity to process and verify transactions. Blockchain, on the other hand, uses a decentralized network to process transactions, making it more efficient and faster.
These are some of the main differences between blockchain and traditional databases. While traditional databases have been widely used for decades, blockchain is still in its early stages of development and has the potential to transform many industries by offering a secure and transparent method of storing and managing data.
What is Blockchain Security
Blockchain security refers to the measures and techniques used to protect blockchain-based systems from various forms of cyberattacks and malicious activities.
The security of a blockchain system is crucial, as it helps to ensure the integrity and accuracy of the data stored on the chain, as well as the trust and confidence of its users.
Here are some of the key components of blockchain security:
- Cryptographic Algorithms: Blockchain uses cryptographic algorithms such as SHA-256, Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA), and others to secure its transactions and protect against tampering and hacking.
- Decentralized Network: A blockchain network is maintained by a decentralized network of computers, rather than a single entity, reducing the risk of a single point of failure and improving the overall security of the system.
- Immutability: Once data has been recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, making it a secure and permanent record of all transactions.
- Consensus Algorithms: Blockchain uses consensus algorithms such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) to validate transactions and add new blocks to the chain. These algorithms help to ensure that all participants on the network have the same version of the blockchain and prevent malicious actors from tampering with the chain.
- Private Keys: Blockchain uses private keys to secure and control access to individual wallets, helping to ensure that only the owner of a wallet can make transactions and access its funds.
These are some of the key components of blockchain security, and they work together to ensure the integrity and security of blockchain-based systems.
Despite these security measures, blockchain is still a relatively new technology, and there are ongoing efforts to improve its security and address any vulnerabilities that may arise.
Companies Using Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has been embraced by many companies across various industries. Here are a few examples of companies that are using blockchain:
- Financial Services: JPMorgan Chase, Mastercard, and American Express are using blockchain to enhance the speed, security, and efficiency of financial transactions.
- Supply Chain Management: Walmart, Maersk, and IBM are using blockchain to improve transparency and traceability in supply chain management, reducing the risk of fraud and counterfeiting.
- Healthcare: Pfizer, Merck, and Roche are exploring the use of blockchain to securely store and share medical records and information.
- Gaming: Gaming companies like Enjin and Dapper Labs are using blockchain to create decentralized, blockchain-based gaming platforms and virtual economies.
- Real Estate: Companies like Propy and BitRent are using blockchain to streamline real estate transactions, reduce the risk of fraud, and improve the efficiency of the buying and selling process.
These are just a few examples of the many companies that are exploring and adopting blockchain technology. The use of blockchain is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to transform many industries and processes in the years to come.
Future of Blockchain Technology
The future of blockchain technology is highly anticipated, as it has the potential to revolutionize various industries and processes. Here are a few ways blockchain technology could shape the future:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Blockchain technology has the potential to disrupt traditional finance by enabling decentralized financial services that don’t rely on intermediaries, such as banks.
- Identity Management: Blockchain Technology could be used to create secure, decentralized identity systems that protect personal data and give individuals control over their information.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain Technology has the potential to improve transparency and efficiency in supply chain management by creating a secure and transparent record of all transactions and interactions.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Blockchain technology could be used to secure and manage the massive amounts of data generated by IoT devices, ensuring the security and privacy of that data.
- Government and Public Services: Blockchain technology has the potential to transform government and public services by enabling secure, transparent, and efficient record-keeping, voting systems, and more.
These are just a few examples of the many potential uses of blockchain technology in the future. While the technology is still in its early stages, it has the potential to transform the way we live and work, making processes more secure, transparent, and efficient.
Blockchain in Different Industries
Blockchain technology has the potential to transform various industries, improving efficiency, security, and transparency in various processes.
Here are a few examples of how blockchain is being used across different industries:
- Financial Services: Blockchain technology is being used to enhance the speed, security, and efficiency of financial transactions. Banks and other financial institutions are exploring the use of blockchain to improve payment systems, reduce the risk of fraud, and streamline the process of securities trading.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain technology is being used to improve transparency and traceability in supply chain management, reducing the risk of fraud and counterfeiting. Companies are using blockchain to create secure and transparent records of all transactions and interactions in their supply chains.
- Healthcare: Blockchain technology is being explored for use in healthcare to securely store and share medical records and information. Blockchain has the potential to improve data privacy, reduce the risk of medical errors, and enhance the efficiency of clinical trials and other medical research.
- Gaming: Gaming companies are using blockchain technology to create decentralized, blockchain-based gaming platforms and virtual economies. This allows for secure, transparent, and verifiable transactions within gaming communities.
- Real Estate: Blockchain technology is being used in the real estate industry to streamline transactions, reduce the risk of fraud, and improve the efficiency of the buying and selling process.
These are just a few examples of how blockchain technology is being used across different industries.
As the technology evolves, it has the potential to transform even more industries, improving the way we live and work.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Blockchain
Blockchain technology offers many potential benefits, but also has some drawbacks and limitations. Here are some of the main advantages and disadvantages of blockchain:
Advantages of Blockchain:
- Decentralization: Blockchain Technology (BT) is decentralized, meaning that there is no central authority or middleman controlling it. This makes it more secure and resistant to hacking, fraud, and censorship.
- Transparency: Blockchain Technology is transparent, allowing all transactions to be publicly visible on the ledger. This makes it possible to build trust and confidence in the system.
- Security: Blockchain technology uses cryptographic algorithms to secure the transactions and protect against tampering. This makes it a secure and reliable platform for storing and transferring data and value.
- Efficiency: Blockchain technology can significantly reduce the cost and complexity of many transactions, since it eliminates the need for intermediaries and streamlines the process.
- Immutability: Once data has been recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, creating a permanent and unalterable record of all transactions.
Disadvantages of Blockchain:
- Scalability: Currently, blockchain technology has scalability issues, meaning that it is not able to process large volumes of transactions quickly and efficiently.
- Complexity: The technology behind blockchain is complex, making it difficult for many people to understand and use.
- Regulation: Blockchain technology is still in the early stages of development, and there is currently a lack of regulation and legal framework for many aspects of blockchain and cryptocurrency.
- Interoperability: Currently, different blockchain systems are not easily compatible with each other, making it difficult to move data and value between different platforms.
- Energy Consumption: The process of mining new blocks and verifying transactions can consume a large amount of energy, raising environmental and sustainability concerns.
These are some of the main advantages and disadvantages of BT. Despite its limitations, blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize many industries and transform the way we store, transfer, and manage data and value.
Blockchain – FAQs
Advantages of Blockchain – Decentralization, Transparency, Security, Efficiency, Immutability
I Hope you have liked our this article. Thank you